- Joined
- Apr 29, 2015
- Messages
- 18,345
- Likes
- 56,533
Enlist all the related variants and modifications here.
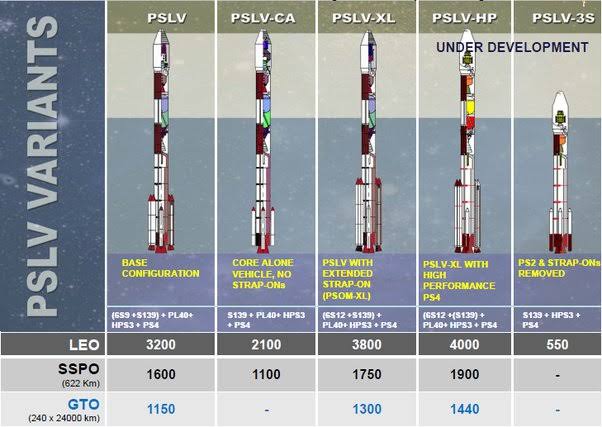
G - Basic; No longer in use
CA: Core alone, with roll control thruster.
modules
XL: Bigger strap on motors and payload capacity
HP: No longer mentioned at ISRO. May be replaced by NGLV program.
3S: Now called SSLV.
DL: Modified CA.
QL: Modified XL
Old photo of PSLV D1.

G - Basic; No longer in use
CA: Core alone, with roll control thruster.
modules
XL: Bigger strap on motors and payload capacity
HP: No longer mentioned at ISRO. May be replaced by NGLV program.
3S: Now called SSLV.
DL: Modified CA.
QL: Modified XL
Old photo of PSLV D1.


